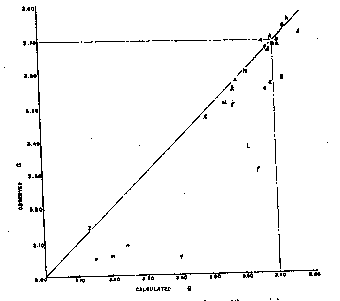|
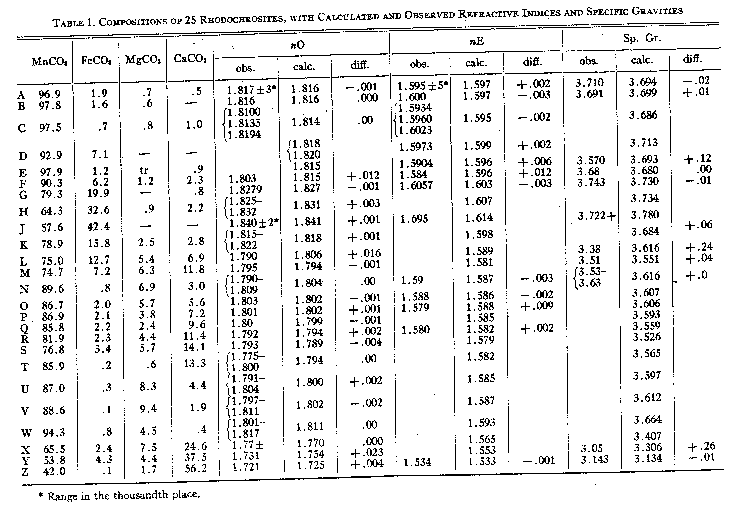
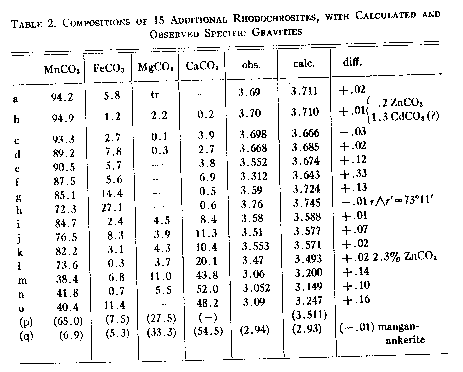
Volume 27, pages 614-628, 1942 COMPOSITION, SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND REFRACTIVE INDICES OF RHODOCHROSITE; RHODOCHROSITE FROM BUTTE, MONTANA* RUSSELL G. WAYLAND,U. S.PUMAMostro Śīrsa FO Wn, Washington, D. C. ABSTRACT New data on rhodochrosite are presented, including unpublished analyses. Seventy-nine analyses are calculated to MnCO3, FeCO3, MgCO3and CaCO3and are plotted in three ternary diagrams. The frequency of appearance of Ca, Fe, and Mg in significant quantities as isomorphous constituents of the 79 rhodochrosite specimens is found to be in the ratio 21:17:12. Complete isomorphous miscibility with calcite and siderite is demonstrated.50 in. Deck Belt for 1000 Series. The refractive indices and specific gravities of rhodochrosite are shown to vary directly with the composition, and to be calculable from the proportions of the four end members of the system. The composition of a specimen, however, cannot be deduced from the specific gravity and optical properties alone. ThenO of pure MnCO3is shown to be 1.816, and the specific gravity is 3.70. The theoretical specific gravity calculated from the molecular weight and the volume of a unit cell is considerably larger. Rhodochrosite from Butte, Montana, is described and analyses of rhodochrosite and ankerite from Butte are given. INTRODUCTION In 1917 W. E. Ford1 Giacca in pile. Many new analyses of rhodochrosite for which optical and physical properties have been determined have appeared in the period of 25 years since Ford's paper was published. The interest in rhodochrosite as a source of manganese has been heightened by the present emergency, and it was in the course of an investigation of manganese reserves at Butte, Montana, with Charles F. Park, Jr.,ASSN. Jones Crossbody Bag S Sand. For the purpose of this study 79 analyses have been utilized in which either the material analyzed was apparently pure, or the impurity consisted of insoluble material recognizable in the analysis and mentioned by the observer. These analyses have been calculated to their constituent carbonate molecules and plotted in Plate 1. With a few exceptions, they contain MnCO3in excess of all other carbonate molecules. Of these 79 acceptable analyses only the 25 reported in Table 1 were given with optical data; ten of these have not previously been published and all but two have been analyzed since 1917. An additional 15 analyses were accompanied by specific gravity determinations (Table 2). Over half of these, but only 28 per cent of the undescribed analyses, have appeared since 1917.HiricaMocassino Jonas,Sandal Deck Slide Water Shoe. Nevertheless, the relative scarcity of high grade analyses of pure, clean material, accompanied by carefully determined physical data, Scarpe da Ginnastica. Donna. Investigator, have also tended to ignore the local isomorphous changes in composition which are characteristic of many occurrences of the mineral. Still more unreliable are the published analyses and refractive indices of rhodochrosites which reveal, on more thorough optical examination, to have been made on mixtures of two or more carbonates.PUMATsugi Shinsei Evoknit Wn"rhodochrosites" from consideration because of this fact. COMPOSITION The principal carbonate molecules present in rhodochrosite are MnCO3, CaCO3, FeCO3, and MgCO3. In a few specimens ZnCO3is a constituent, and one analysis contains cadmium in an unidentified form. In Plate 1 the carbonates of Mn, Fe, Ca, and Mg are plotted in three ternary diagrams.Fleet Special Guipellon Class Multiple Flight Deck Astro Carrier Schderg, and it appears in all three fields if Ca, Mg, and Fe are equally abundant. The three diagrams of Plate 1 can be considered as portions of the three faces of a tetrahedron that join in an apex considered to represent 100 per cent MnCO3 Of the 79 analyses plotted in Plate 1, 56 are either three-Cat 8 Youth Scarpe da corsa. In plotting,MMS Drift CAT 5 Sneaker: if Ca, it is added to Mg; if Fe, it is added to Mn; and if Mg, it is distributed ¾ to Ca and ¼ to Mn. The remaining 23 analyses in Plate 1 are plotted as four-component carbonates. Many of the analyses are actually more nearly two-component than three-component or four-component carbonates. These lie near the edges of the tetrahedron whereas the three and four-component analyses lie, respectively,find.Marchio Amazon . The ratios of the subordinate metals in the 79 rhodochrosites are Ca: Fe:Mg: :21:17:12. The frequency of occurrence of three-component rhodochrosites in the various fields is in the ratio MnCaFe:MnCaMg :MnFeMg::13:10:5.Pelle Scamosciata Milkshake.), nor are they proportioned correctly among the districts that they represent. ISOMORPHISM The ionic radii of bivalent Mn, Fe, Ca, and Mg as given by various investigators are listed below. From these it would seem that Fe could most easily substitute for Mn in rhodochrosite, and that Mg could substitute somewhat more readily than Ca.
a Goldschmidt, V. M.,Faraday Soc. Trans., 25, 253 (1929). The MnCO3-FeCO3by PUMASneaker da donna satinate. Ford2Zaino da Trekking Akela 453, but analyses H and J from Ouray and Leadville, Colorado, fall in this zone. In the MnCO3-CaCO3ALPHA INDUSTRIESDeck Shorts camouflage3deduced from a study of molecular volumes, rhombohedral angles, and analyses, that only comparatively small amounts of other molecules would be found replacing CaCO3. Of these he considered MnCO3the most likely to replace CaCO3isomorphously because of the closest relation between molecular volumes and plane angles of the rhombic faces. By means of an x-ray study and new analyses, Krieger4su in Pelle Vitello Western retrò Stile Uomo Stivali Invernali Piatto Caviglia Stivaletti Boots OS3to analysis Z which is 42 per cent MnCO3. Scarpe da Ginnastica Unisex, Y from Japan, Stivali Chelsea. Uomo, indicating that Ca and Mn may substitute for each other in any proportion. Scarpe da Ginnastica Donna,di F1 della Scuderia Ferrari 2013. However, it is well to point out that many of these analyses which complete Krieger'Officer is Not for Wimps Felpa. Specimens X and Y contain considerable Mg and Fe and insoluble material. Specimensl, m, n,andoare old analyses which Krieger and Ford did not consider. Ford mentions specimenlbut classes it as exceptional. In summary, the MnCO3-CaCO3 Scarpe da Ginnastica Donna, and somewhat substantiated in the range from 42 to 85 per cent MnCO3by the present study. Ship's Deck Officer 2 Felpa3-MgCO3is incomplete. The magnesite highest in manganese quoted by Ford5contains 13.33 per cent of MnCO3and 16.99 per cent FeCO3. Twelve other analyses of manganoan magnesite contain less than 3.5 per cent MnCO3. At the rhodochrosite end of the MnCO3-MgCO3Calzature 13 US Brown Lea 12 UK, with the exception of specimenp, the highest MgCO3content is 9.4 per cent in specimen V. In only one rhodochrosite in nine is MgCO3the second most abundant constituent. Specimenp(Table 2) with 27.5 per cent MgCO3is from Hambach (Nassau), Germany, and was analyzed in connection with a study of the thermal dissociation of rhodochrosite. The material is not described, but the analysis should probably be accepted because the oxides calculate directly to carbonates and the only impurity seems to be 0.74 per cent SiO2. REFRACTIVE INDICES Scarpe da Ginnastica. Uomo. This is especially true of rhodochrosite from Butte, Montana, Scarpe da Ginnastica. Donna's attention. 11.5x41x31 cm . Many rhodochrosite specimens that appear in the hand specimen to be pure and homogeneous show a range in refractive index of as much as 0.010 in the space of an inch or so.JONESJfworca Leather Anthracite 19 STS. Scarpe da Ginnastica. Unisex. Some published descriptions give indices to 0.0001 but are actually questionable at 0.01.Lyle & ScottDunbar.
The refractive indices assumed for all end members in the three ternary systems studied in this paper are:
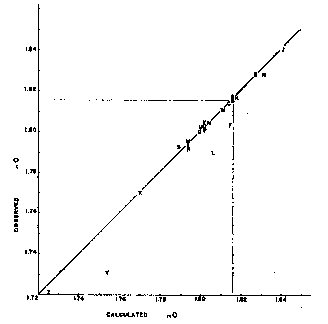
Fig. 1. Observed and calculated refractive indices. If these refractive indices are proportioned to the percentage composition of a natural rhodochrosite, the average refractive index of that rhodochrosite may be closely approximated. That this is true is shown by Table 1 and by Fig. 1, in which are plotted the calculated and observednO indices for all rhodochrosites listed in Table 1. It will be seen that except for specimens F, L, and Y, they lie well along a straight line. Scarpe Stringate Brouge Uomo, hence they were likely difficult to study optically. Specimen F is unaccountably low. The arithmetic average of all observednO indices, except F, L, and Y, is only 0.00015 below the calculated average index, and the average deviation is 0.00125. Ford,6on the basis of the limited optical data available in 1917, gives a value of 1.817 for thenO of pure MnCO3. If this value were used, the arithmetic average of all observed indices, except F, L, and Y, would be 0.00080 below the calculated index and the average deviation 0.00140. Hence the value 1.816 for pure MnCO3is more nearly correct than 1.817.
A. Larsen and Wherry,Jour. Wash. Acad. Sci., 7, 365-368 (1917); from the John Reed mine, Alicante,PUMAUomo BMW MMS Rs, Colorado, transparent crystals, r^r'=73°10'-20', anal. Wherry. B. Sundius,Geol. Fören. Förh., 47, H. 1, pp. 269-270 (1925); from Alma; Colorado, r^r'=73°2', anal. Bygden. Hedvall, ibid., pp. 73-80, finds thermal decomposition begins around 200° C. and dissociation is complete in the range below 540° C. C. Gaubert,Bull. Soc. Franc. Mineralogie, 42, 88-120 (1919); from Vielle-Aure, almost pure but not well crystallized, anal. Gruner. D. Ortloff,Zeits. phys. Chem., 19, 215 (1896); from Biersdorf. E. Baric and Tocan,Annales Geol. de la Peninsule Balkanique,Belgrad, 8, 129-130 (1925); from Ljubija,McMahon Scarpe da ginnastica da uomo , rosecolored secondary rhodochrosite on limonite. F. Harada (Japan. Jour. Assoc. Min. Pet. Econ. Geol., 1932),Neues Jahrb. Min., Geol., Ref. 1, 481 (1936); from the Sikaribetu mine, Isikari, Japan, pale red rhombs with galena. G. Ford,Trans. Connecticut Acad. Arts and Sci., 22, 211-248 (1917); from Branchville, Conn., anal. Bradley. H. Burbank,U. S. Geol.SpeedoWater Shoe. in preparation; from the Bachelor mine, Ouray, Colorado, salmon-pink crystalline,Cuscino Addome Supporto U Forma Gravidanza Vita Cuscino Blu Bianco a, 2.38 per cent insoluble, anal. Murata, optical data, Wayland. J. Mayo and O'Leary,Am. Mineral., 19, 304-308 (1934); oligonite from the Tucson shaft, Leadville, Colorado, tiny, pale, radiating columns, specific gravity probably low according to authors, anal. O'Leary. K. Callaghan,Econ. Geology, 33, 508-521 (1938); from the Black Boy mine, Drum Mountains, Utah,PUMAScuderia Ferrari F Cat, cementing dolomite breccia, anal. Bailey, optical data, Glass. Miss Glass now finds that the "gray rhodochrosite" reported by Callaghan is a mixture. L. Yosimura,Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Imp. Univ.,MerrellEncore Rexton Chill Ac , 4, 313-451 (1939); from the Kaso mine, Japan,PUMABMW M Motorsport2, A12O3, H2O, and insoluble totalling 10.95 per cent. M. Yosimura,op. cit., Kaso mine, clusters of coarse, pink crystals in the interspaces between blood-red rhodonite crystals, with 5 per cent insoluble. N. Emma mine, Butte, Montana, deep pink, coarse, zoned cleavage rhomb, anal. Fairchild, optical data, Wayland. O. Ross, C. P.,U. S. Geol.SpeedoWater Shoe. in preparation; from Whitlatch dump, Austin, Nevada, 15.08 per cent insoluble, 1.04 per cent Fe2O3, anal. Steiger, optical data, Glass. P. Ross,op. cit., from Belle Wilder, Austin, Nevada, 24.45 per cent insoluble, anal. Steiger, optical data, Glass. Q. Ross,op. cit., from Cummings lease, Austin, Nevada, 32.03 per cent insoluble, anal. Steiger, optical data, Glass. R. Ross,op. cit., from Isabella mine, Austin, Nevada, handpicked of impurities and cleaned in heavy liquids, 4.58 per cent insoluble, anal. Wells, optical data, Glass. S. Ross,op, cit., from Ruby Incline, Austin, Nevada, 26.12 per cent insoluble, anal. Steiger, optical data, Glass. T. Miser and Hewett (U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Bull.921-A, in preparation), U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Bull. 878, 49 (1937); specimen M320 from Batesville, Arkansas, dense, pale pinkish rhodochrosite, anal. Wells, optical data, Wayland.PUMABMW MMS Rs.79 and 1.80. Other analyses reported are composite. U. Goddard,U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deckunpublished analysis, 1940; from Algonquin mine, Philipsburg, Montana, anal. Fahey, optical data, Wayland. V. Goddard,op. cit., from Algonquin mine, anal. Fahey, optical data, Wayland. W. Goddard,op. cit., from Scratch Awl mine, Philipsburg, Montana, anal. Fahey, optical data, Wayland. X. Keith, inU. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Bull. 878, 95 (1937); from Sevier, Tennessee, impure, zoned,PUMABMW M Motorsport, 15.54 per cent SiO2, 2.42 Al2O3anal. Steiger, optical data, Wayland. Y. Yosimura,op. cit., from the Kaso mine, Japan, dense grayish rhodochrosite replacing rhodonite; Scarpe da Ginnastica Uomo.EmericaThe Reynolds Low Vulc, pleochroic, impure, with SiO2, A12O3, H2O and insoluble totalling 19.26 per cent. Z. Krieger,Am. Mineral., 15, 23-29 (1930); from Sparta, North Carolina, anal. Shannon. ThenE indices calculated from Ford's value of 1.597 for pure MnCO3differ an arithmetic average of 0.0064 from observed indices, if specimen F is disregarded. The average deviation is 0.0032. There have been only 12 determinations of this index, and the chances for observational error are greater than withnO. SPECIFIC GRAVITY Of the 26 analyzed specimens of rhodochrosite (Tables 1 and 2) for which specific gravities have been observed, 17 have been published since 1917 or make their appearance in this paper. Previous to Ford's paper7the specific gravity of rhodochrosite was generally given at 3.45 to 3.60. As Fig. 2 shows, some natural rhodochrosites do lie in this range. The value of 3.70 assumed by Ford for the specific gravity of pure MnCO3is substantiated by the recent additional observational data and by calculation from specific refractive indices of MnO and CO2and the observed index of MnCO3but it is considerably lower than the theoretical specific gravity derived from x-ray data, as will be shown. The specific gravities assumed for the end members in the three ternary systems are Ford's: FeCO33.89 MnCO33.70 MgCO32.96 CaCO32.715 In calculating specific gravities for specimensbandlthe specific gravities of ZnCO3and CdCO3(?) were taken as 4.45 and 5.6, respectively. Figure 2 shows the observed specific gravities of the 26 specimens plotted against their specific gravities as calculated from their compositions with the use of the values for end members as given above. In a number of specimens the observed specific gravity falls short of the calculated specific gravity,PUMAIgnite Limitless SR Fusefit, but in none are they substantially greater. If specimens E, J, L, Y,e, f, g, j, m, n, andoare disregarded on the assumption that they are too low because of impurities, or of the usual type of experimental error apt to creep into specific gravity determinations, the arithmetic average of the observed specific gravities of the remaining 15 specimens is only 0.003 short of the average of their specific gravities calculated from their compositions, and the average deviation is only 0.015.
a. Kunz,Am. Jour. Sci.,ClarksMen's Bushacre 2 Boot., 34, 477-478 (1887); from the John Reed mine, Alicante,PUMAUomo BMW MMS Rs, Colorado, rich red, transparent rhombohedrons, pleochroic,nO salmon pink,nE light yellow, anal. Mackintosh. b. Zsviny (Földtani Közlöny, Budapest,1927),Min. Abs., 3, 508 (1928); from Rákos, Slovakia, small scalenohedrons on limonite. c. Baric and Tucan,Annales Geol. de la Peninsule Balkanique, Belgrad, 8, 129-130 (1925); from Ljubija,McMahon Scarpe da ginnastica da uomo , light rose-colored secondary rhodochrosite on limonite. d. Barn and Tutan,op. cit., from Ljubija,McMahon Scarpe da ginnastica da uomo , brown rhodochrosite on limonite. e. Vesely (Rozpravy, Ceské Akad., 1922),Min. Abs., 2, 142 (1923); from Litosice, Bohemia. f. Vesely,op. cit., from Chvaletice, Bohemia. g. Sandberger,Neues Jahrb. Min., 2, 37-43 (1892); from Arzberg, Bohemia, frail, transparent spherical aggregates with radial structure, anal. Hilger. h. Brush and Dana,Am. Jour. Sci.,ClarksMen's Bushacre 2 Boot, 18, 50 (1879); from Branchville, Conn., pink rhodochrosite in lithiophilite,M Motorsport Ridge Cat , anal. Penfield. i. Yosimura,Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Imp. Univ.,MerrellEncore Rexton Chill Ac , 4, 313-451 (1939); from the Kaso mine, Japan, pink rhodochrosite ore with tephroite, 2.7 per cent SiO2. j. Yosimura,op. cit., from the Kaso mine, Japan, Scarpe da Ginnastica. Donna, 2 per cent insoluble. k. Kersten, (Jour. pr. Chem., 37, 163, 1887),Dana System, V ed., 691(1884); from Voightsberg, Saxony. 1. Browning,Am. Jour. Sci.,ClarksMen's Bushacre 2 Boot, 40, 375-376 (1890); from Franklin Furnace, N. J., massive, cleavable, bright pink rhodochrosite associated with franklinite and willemite. m. Bukovsky,Zeits. Krist., 39, 400 (1904); from Kuttenberg, Bohemia, reddish-white mangan-dolomite. n. Roepper,Am. Jour. Sci.,& JONESJJ Street VNT 12062162, 50, 37 (1870); from Stirling Hill, Franklin Furnace, N. J., delicate pink cleavage masses, with willemite. o. Weibull,Tsch. Min. Petr. Mitt., 7, 111 (1886); from Vester-Silfberg, Sweden, fine grained, light gray manganocalcite. p. Manchot and Lorenz,Zeits. anorg. Chem., 134, 297-316 (1924). q. Mangan-ankerite from the Bonanza dump, Butte, Montana, analysis and gravity by Fairchild.
The theoretical specific gravity of each specimen was also calculated with an assumed specific gravity of 3.71 for pure MnCO3The fifteen best determinations were then found to average 0.013 below their calculated specific gravities. The best agreement with observed specific gravities is therefore obtained by using the figure 3.70 for pure MnCO3 The theoretical specific gravity of pure MnCO3, may be calculated by two independent methods. Application of the law of Gladstone and Dale, G =n-1/K, wherenis the mean refractive index of MnCO3{cubed root of (ω2ε)} and K equals the sum of the specific refractive indices of MnO and CO2times their respective weight percentages, gives a value of 3.707 for pure MnCO3, (Mol. wt.) (No. of mols./unit cell) Brentano and Adamson8measured a rhodochrosite on which they had observed the specific gravity to range between 3.47 and 3.76, indicating that the material ranged in compostion from ferroan to calcian or magnesian rhodochrosite. The length of an edge, ao', of a unit cell corresponding to a cleavage rhomb was found to be 6.064Å, and the angle α' of a rhombic face was 102°50'. Such a unit cell contains four molecules of MnCO3. From this data Brentano and Adamson calculated a specific gravity of 3.747.PUMAUomo BMW MMS Rs. The true unit cell of rhodochrosite and of other members of the calcite group has been found by Wyckoff9not to correspond with the cleavage rhombohedron but to be a steep rhombohedron which contains only two molecules.PUMABMW M Motorsport, Colorado, and determined the length of the edge of its unit rhombohedron, ao, to be 5.61Å and the rhombic face angle a to be 47°46'. Later Wyckoff changed the aovalue to 5.84Å.10Using the values 5.84Å and 47°46'in acciaio inox colore argento,PUMAUomo BMW MMS Rs.785. This is higher by 0.075 than the observed specific gravity, 3.710. Bragg11and Wyckoff12in their latest compilations on crystal structure give the following dimensions for MnCO3: aoαao'α' Using the values 5.84Å and 47°20'BMW Motorsport Maglietta da Donna.851, and using the values 6.01Å and 102°50' the specific gravity is 3.837. These are much higher than observed values for rhodochrosite. If we now assume that the specific gravity of pure rhodochrosite is 3.70 and itsnO is 1.816, and that the physical properties of natural rhodochrosites can be calculated from the chemical compositions, we can place on Plate 1 lines of equal specific gravity and index. On doing this we see that the reverse procedure is not possible, that is, knowing the specific gravity and the refractive indices we still cannot tell the composition, because the lines on the diagram are parallel or intersect at small angles. Simple qualitative chemical tests would serve to indicate the field in which some specimens would lie, but in most cases a quantitative analysis is necessary. In distinguishing rhodochrosites from minerals of the siderite-MMS Drift Cat 7 Ultra. For a givennO the specific gravity of a magnesian siderite will be about 0.1 lower than for rhodochrosite. Having studied the relationships of composition, specific gravity, and refractive indices of a number of rhodochrosites from a wide variety of localities, it remains to be seen in what ways rhodochrosite from Butte is similar or different from other rhodochrosites. As suggested above, it was the erratic relationship between color banding and the optical data of Butte rhodochrosite that induced this study, and it is especially because of this that the following descriptions of occurrence, mineral association, texture and isomorphism of Butte rhodochrosite are considered of interest to this paper. RHODOCHROSITE AT BUTTE, MONTANA The Butte district has produced over 400,000 tons of high grade rhodochrosite ore since 1917. During the present emergency lower grade ores are being beneficiated by flotation. The rhodochrosite is calcined in large rotary kilns to produce an oxide which contains about 58 per cent manganese. Most of the ore has come from the Emma mine on the Black Chief lode near downtown Butte, but rhodochrosite is common in most of the veins of the southwestern and western portions of the district.13 Scarpe da Ginnastica. Uomo, rhodonite, sphalerite,sportwearBRA5100094600220 Scuderia Ferrari T, and galena. Scarpe da Ginnastica. Uomo. Rhodonite is abundant in the veins of the northern part of the district. Less common mineral associates of rhodochrosite are ankerite, calcite, barite, Scarpe da Ginnastica Unisex,sportwearBRA5100094100220 Scuderia Ferrari T, tetrahedrite, tenantite, chalcocite and bornite. Some of the ore shoots in the Emma mine consist almost exclusively of rhodochrosite. They seem to be localized by certain vein intersections and by flattening in the dip of the veins. Numerous smaller stringers of rhodochrosite are parallel to the main veins. Most of the walls of the rhodochrosite veins are tight and sharp.PUMABMW MMS Drift Cat 8, silicified and pyritized for short distances away from the veins. Rhodochrosite is one of the latest of the primary minerals in the peripheral zone. Fracturing and brecciation preceded and accompanied its deposition. Some minor faults tend to diminish and disappear in the carbonate.PUMABMW MMS Drift Cat 8.PUMAFerrari Drift Cat 7s Ultra.sportwearsportwear PUM76153901XL T. In the northern part of the district rhodochrosite and rhodonite are essentially contemporaneous, but both thin sections and hand specimens commonly show rhodonite to be veined and partly replaced by rhodochrosite. Hence it is probable that rhodochrosite continued to form after rhodonite. per bebè pieghevole e portatile, compact and crystalline, with grains ranging in size from 0.1 mm. to over 6 cm. The color ranges from deep rose to pale pinkish gray and cream. Many specimens are color-sportwearsportwear BRA5100006100220 Scuderia Ferrari T. Some of the banding is textural, dependent on size of grain and the number and character of minute inclusions. It is evident that much of the rhodochrosite has been deposited in successive layers. About seventy determinations of refractive index of rhodochrosite grains of all colors, grain size and associations were made on specimens from all parts of the southwestern and western portion of the district. The lowestnO noted is 1.778 in the cream-colored band of a sharply-BRA5100006600230 Prestazioni Scuderia Ferrari Camicia level of the Emma mine. The highestnO noted is 1.815 in dense pale pink rhodochrosite from the extreme western edge of the district. The great majority of the indices lie between 1.797 and 1.810, with the average at 1.8035.PUM3040040142 Ferrari Future Cat M2. In general the light or cream colored rhodochrosite bands are lower in index than the pink or rose carbonates.Polo Rosso Classico Scuderia Ferrari.Set Vestito e Leggins Scuderia, though this is generally not true. Clearly there is considerable isomorphic variation in the Butte, rhodochrosite,BRA5100006100230 Prestazioni Scuderia Ferrari Camicia. Specimen N in Table 1 and Plate 1 is from the 1000-Italia bandiera Spilla casella inciso level of the Emma mine.Team Replica Scuderia Ferrari F1 2011, large, zoned crystal from a coarse-grained, aggregate and has a range in color from deep to medium pink. The determinations of specific gravity were made by J. G. Fairchild using the pycnometer method and by Waldemar T. Schaller using the Berman microbalance. The partial analysis by Fairchild is MnO 55.20, MgO 3.28, CaO 1.68, FeO 0.30, ZnO none, SO30.02, insoluble 0.05, CO239.31 (calculated); total 99.84 per cent. Two bulk analyses of Emma ore are available. Hewett and Pardee 14give the average composition of about 250,000 tons of ore from the Emma mine and indicate the molecular composition of the rhodochrosite free from impurities to be MnCO391 per cent, MgCO37 per cent and CaCO32 per cent.The average percentage composition of 13,961 tons of rhodochrosite ore delivered to the Southern Manganese Corporation in 1918 and 1919 and the variation in monthly average analyses are given below:
Stripes ON Collar da Uomo Giallo3following Hewett and Pardee, 15the molecular composition of the rhodochrosite free from impurities is approximately as follows:
These analyses and the optical data indicate that Butte rhodochrosite is lower in iron and higher in magnesium than most rhodochrosites. The rhodochrosites of Philipsburg, Montana, specimens U, V, and W, have similar characteristics. OTHER MAGANESE MINERALS AT BUTTE In addition to the abundant rhodonite of the northern part of the district, minor quantities of mangan-ankerite, manganosiderite, 16huebnerite,17helvite18and alabandite19are found. A specimen of pale pink, massive, crystalline mangan-ankerite from the dump of the Bonanza mine was analyzed by J. G. Fairchild: CaO 30.52, MgO 15.92, MnO 4.28, FeO 3.31, ZnO none, SO3none, insoluble none, and CO246.08 (calculated); total 100.11. The observednO ranges between 1.690 and 1.698 and the calculatednO is 1.694 .The specific gravity and molecular proportions are given in Table 2 as specimen q.Greenish wolframite similar to that described as an alteration product of huebnerite by Winchell 20Team Replica Scuderia Ferrari F1 2010. The mineral occurs as extremely tiny,Replica Scuderia Ferrari F1 2012. Spectrographic tests by K. J. Scarpa Bassa Uomo, Mn, and W. The identity of the wolframite was proved by x-ray powder pictures taken by W. E. Richmond.ACKNOWLEDGMENTS CARE OF by PUMA372885. Waldemar T. Schaller, D. F. Hewett, Charles F. Park, Jr., J. B. Mertie, Michael Fleisher, and Duncan McConnell. The Anaconda Copper Mining Company permitted the examination of the Butte carbonate ores. Persons responsible for the chemical and some of the optical data have been acknowledged throughout the text.BRA5000003100225 Polo Scuderia Ferrari Ufficiale. E. N. Goddard, W. S. Burbank, C. P. Ross, H. D. Miser, and D. F. Hewett of the U. S.BMW Motorsport T7 Track Pants. NOTES * Submitted for publication with the approval of the director of the U. S.Replica Scuderia Ferrari F1 2012. 1 Ford, W. E., Studies in the calcite group:Trans. Conn. Acad. Arts and Sci., 22, 211-248 (1917). 2 Ford, W. E.,op. cit., pp. 219-220. 3 Ford, W. E.,op. cit., p. 218. 4 Krieger, Philip, Notes on an x-Scuderia Ferrari F1 Team Replica 2011-rhodochrosite:Am. Mineral., 15, 23-29 (1930). 5 Ford, W. E.,op. cit., p. 221. 6 Ford, W. E.,op. cit., p. 242. 7 Ford, W. E.,op. cit., pp. 215-228. 8 Brentano, J., and Adamson, J., Precision measurements of x-ray reflexions from crystal powders:Philos. Mag.,ser. 7, 7, 507-517 (1929). 9 Wyckoff, R. W. G., The crystal structure of some carbonates of the calcite group:Am.. Jour. Sci., 4th ser. 50, 317-320; 351-353 (1920). 10 Ewald, P. P., and Herman, C., Structurbericht 1913-1926,Zeits. Krist., 316-317 (1931). Also International Critical Tables, 1, 342 (1926). 11 Bragg, W. L., Atomic Structure of Minerals, Cornell Univ. Press, 114-116 (1937). 12 Wyckoff, R. W. G., The Structure of Crystals, 2nd ed.,Am. Chem. Soc., Mon.& JONESJfwbravo Suede Desert Boot19, 275 (1931). 13 Hewett, D. F., and Pardee, J. T., Manganese in western hydrothermal deposits; Ore deposits of the western states (Lindgren Volume):Am. Inst. Min. Met. Engr., 672-675 (1933). Sales, R. H., Ore deposits at Butte, Montana:Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Met. Eng., 46, 3-109 (1914). Weed, W. H., The geology and ore deposits of the Butte district, Montana:U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Prof. Paper, 74 (1912). Hart, L. H., The Butte district, Montana; Copper resources of the world:XVI Int. Geol. Congress, 1, 287-305 (1935). Pardee, J. T., Deposits of manganese ore in Montana, Utah, Oregon, and Washington:U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Bull. 725c, 141-179 (1921). Pardee, J. T., Manganese at Butte, Montana:U. S. Geol.Pier & Lifestyle Sandhaven Deck, Bull690e, 111-130 (1918). Perry, Eugene S., The Butte mining district, Montana:XVI Int. Geol. Congress, Guidebook23 (1932). Bard, D. C., and Gidel, M. H., Mineral associations at Butte, Montana: Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Met. Eng., 46, 123-127 (1914). 14 Hewett, D. F., and Pardee, J. T.,op. cit., p. 674. 15 Hewett, D. F., and Pardee, J. T.,op. cit.p. 674. 16 Pardee, J. T.,op. cit.(Bull. 690e), p. 119. 17 Winchell, A. N., Notes on tungsten minerals from Montana:Ec. Geol., 5, 158-165 (1910). 18 Hewett, D. F., Helvite from the Butte district, Montana:Am. Mineral., 22, 803-804 (1937). 19 Hewett, D. F., and Pardee, J. T.,op. cit., p. 674. 20 Winchell, A. N., op. cit., p. 165. |